Compostable, biodegradable, and bioplastic are terms commonly used to describe materials that are more environmentally friendly compared to traditional plastics.
However, there are important distinctions between them:
Compostable:
Compostable materials are capable of breaking down into natural elements in a composting environment. They undergo a specific process called composting, where they degrade into organic matter within a defined timeframe, usually under controlled conditions. Compostable items contribute to the creation of nutrient-rich compost that can be used for agricultural purposes.

Biodegradable:
Biodegradable materials have the ability to break down naturally over time, with the help of microorganisms, into simpler components such as water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. Unlike compostable materials, biodegradable items don’t require specific composting conditions. They can biodegrade in various environments, including landfills. However, the duration of biodegradation varies depending on the material and environmental conditions.

Bioplastic:
Bioplastics are a type of plastic derived from renewable resources like plants or biomass. They are designed to offer an alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics, which have significant ecological impacts. Bioplastics can be either compostable or biodegradable, but not all bioplastics fall into these categories. Some non-biodegradable bioplastics are still made from renewable resources, offering the advantage of reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
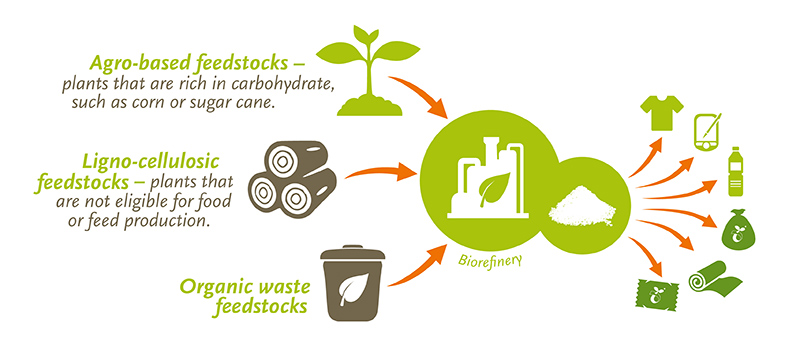
In summary, compostable materials can fully break down into organic matter in a composting facility, biodegradable materials break down naturally over time through microbial activities, and bioplastics are plastics derived from renewable resources that can be either compostable or biodegradable, depending on their composition. It’s crucial to understand the specific characteristics and certifications of products labeled as compostable, biodegradable, or bioplastic to make informed choices regarding their disposal and environmental impact.
